Search
Tina5s enables teams to efficiently find and retrieve files using a variety of document metadata driven search features. Simple search allows users to quickly find files based on document metadata and content. Advanced search provides filters and queries for more precise searches. Relationship-based search allows users to explore file organization in a hierarchical or flat manner. Additionally, Tina5s supports cross-company and cross-system file search and document collaboration. These features empower teams to locate required files rapidly, improving productivity and facilitating seamless information sharing.
Rich Search
How long does your project team spend just looking for the information they need to get their work done? Studies show that it could be as high as an hour a day for every engineer on your team. Tina5s' document metadata driven search features make finding documents and files easy cutting search times to just seconds. Improved project team productivity enables project cost control.
Personal File Organization
Traditional folder-based file organization is a proven method that works well for individual file management. In Tina5s, you have the flexibility to create and customize your own folder structure to suit your needs. Link frequently used or important files to any folder you like: consider it your personal desktop within Tina5s. Choose folder names that resonate with you and organize them in a way that helps you quickly locate the files you need today.
Simple Search Based On Document Metadata
Finding documents and files in Tina5s is fast and simple. Just type what you're looking for into the user-friendly search pane. Your search results will be ranked by relevance based on document metadata (or content - you choose). Plus, you can define an unlimited number of metadata fields during setup to significantly enhance Tina5s' search capabilities.
Filter Document Metadata Values
Narrow your searches by applying document metadata based filters to your search terms. Available filters include content search on/off, document categories, document lifecycle, records with and without files and more.
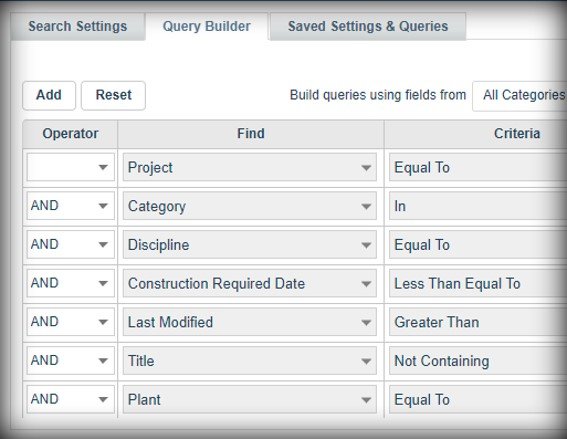
Document Metadata Based Search Queries
Searching for a specific engineering report but can't recall its title? If you know the author and that it was released last month, Tina5s has you covered. Use the platform to craft detailed document metadata based search queries with the information you do remember. Combine search terms using AND, OR, NOT, and other operators to quickly locate the files and documents you need. If you use defined queries often, save them for future use.
Group, Sort and Filter Results
In Tina5s, search results appear in a familiar Excel-like grid, ranked to display the most relevant documents at or near the top. If your initial search is too broad and you don't find your desired document on the first page, don't worry. Utilize Tina5s' search results grid grouping, sorting, and filtering features, much like those in Excel, to quickly mine document metadata values to refine your search and locate the document you need.
Linear Relationships
Tina5s enables you to establish and manage connections between your project documents and files, making it easier to trace a path to the specific document you need. For example, contracts may link to related specification documents, which in turn connect to corresponding design drawings. This interrelated structure helps you to navigate through project information to find the document you need.
Hierarchical File Organizations and Where Used
Tina5s enhances file organization by allowing you to create hierarchical structures of files and documents. This makes it easy to navigate up and down the chain to find the files you need swiftly. Hierarchies can be configured to update automatically as documents are revised. Rules based on document metadata can also be established to add new documents to the hierarchy automatically. Additionally, a single document can be part of multiple hierarchies - to identify the hierarchies where a document appears, you can use Tina5s' 'Where Used' feature.